The 2023 First Aid PDF guide provides updated protocols, essential techniques, and practical advice for emergency care․ It emphasizes preparedness, safety, and effective responses to various incidents, ensuring everyone can act confidently in critical situations while staying informed about the latest medical recommendations and safety standards․
Overview of First Aid Importance
First aid is a critical skill that can save lives, reduce recovery time, and prevent minor injuries from becoming severe․ It empowers individuals to act confidently in emergencies, providing immediate care until professional help arrives․ Proper first aid minimizes pain, reduces the risk of complications, and promotes faster healing․ It also reassures casualties, reducing psychological trauma․ In workplaces and homes, first aid fosters a culture of safety and preparedness․ Regular training ensures that everyone can respond effectively, making communities safer and more resilient․ Understanding its importance encourages proactive learning and application, ultimately saving lives and improving outcomes in everyday emergencies․
Key Updates in First Aid Guidelines for 2023
The 2023 first aid guidelines introduce updated protocols to reflect the latest medical research and best practices․ Key changes include revised CPR techniques, emphasizing continuous chest compressions and updated compression depths․ New recommendations for wound care highlight the use of advanced dressings and antimicrobial agents to prevent infection․ Guidance on mental health first aid has been expanded, focusing on early intervention and support for emotional distress․ Additionally, there is a stronger emphasis on the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs) and public access to these devices․ These updates aim to improve outcomes, reduce risks, and enhance the effectiveness of first aid interventions in various emergency situations․

First Aid Kit Essentials
A well-stocked first aid kit should include bandages, antiseptics, gloves, and a first aid manual․ Ensure items are organized, easily accessible, and up-to-date with 2023 guidelines․
Must-Have Items in a Basic First Aid Kit
A basic first aid kit should include essential items like bandages, antiseptic wipes, medical gloves, a first aid manual, and over-the-counter medications such as pain relievers and antihistamines․ Additional must-haves include gauze pads, rolled gauze, scissors, tweezers, and a thermometer․ These items are crucial for treating minor injuries, such as cuts, burns, and scrapes․ Ensure all supplies are stored in a clean, durable container and are easily accessible․ Regularly check expiration dates and restock as needed to maintain readiness for emergencies․ Tailor the kit to address common household or workplace incidents, adhering to 2023 first aid guidelines for optimal preparedness․
Additional Supplies for Advanced First Aid Kits
An advanced first aid kit should include specialized items for severe injuries, such as splints for fractures, cold packs for swelling, and tourniquets for controlling heavy bleeding․ Add burn blankets, over-the-counter medications like antihistamines, and prescription medications if necessary․ Include IV fluids and advanced dressings for deep wounds․ Eye wash solutions and protective gear like gloves and masks are essential․ For cardiac emergencies, consider including an automated external defibrillator (AED)․ Incorporate items like oxygen tanks and advanced airway devices for respiratory distress․ Ensure all supplies are organized for quick access and tailored to address specific risks or environments, following 2023 first aid guidelines․

Common First Aid Emergencies
Common first aid emergencies include burns, cuts, cardiac issues, and choking․ Immediate, effective responses are crucial to prevent worsening conditions and ensure proper recovery, following 2023 guidelines․
Burns and Scalds: Immediate Response
Immediate response to burns and scalds involves stopping the burning process by removing the source and cooling the affected area with cool, running water for 10-20 minutes․ Never use ice or icy water․ Assess the severity by checking the size and depth of the burn․ Cover the burn with a non-stick, sterile dressing to prevent infection․ For severe burns (covering large areas or extending beyond the superficial layer), seek immediate medical attention․ Do not apply creams or ointments, as these can interfere with professional treatment․ Stay calm and monitor the individual’s condition until help arrives, following the latest 2023 first aid guidelines․
Wounds and Cuts: Cleaning and Dressing
Proper cleaning and dressing of wounds and cuts are crucial to prevent infection and promote healing․ Begin by washing your hands and rinsing the wound under clean, running water to remove dirt and debris․ Avoid using harsh soap, hydrogen peroxide, or iodine, as these can irritate the tissue․ Pat the area dry with a clean towel and apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment․ Cover the wound with a sterile bandage or dressing, securing it in place․ Monitor for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus, and change the dressing daily․ Seek professional care for deep or jagged wounds․
Cardiac Emergencies: CPR and AED Use
Cardiac emergencies require immediate action to save lives․ If a person collapses and is unresponsive, call emergency services and begin CPR if trained․ Place the person on their back on a firm surface, position your hands in the center of their chest, and perform compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute․ Use an automated external defibrillator (AED) if available, following the device’s voice prompts․ Attach the pads to the bare chest as instructed and deliver a shock if advised․ Continue CPR until medical help arrives․ Early intervention significantly improves survival rates and neurological outcomes for cardiac arrest victims․
Choking: Relief Techniques for Adults and Children
Choking emergencies require swift action to restore breathing․ If an adult or child is choking, stand behind them and wrap your arms around their waist․ For adults and children, perform abdominal thrusts: place one fist between the navel and ribcage, grasp it with your other hand, and thrust inward and upward․ For infants under one year, use chest thrusts instead of back slaps․ If the person becomes unresponsive, begin CPR․ Always call for emergency help if choking persists․ Early intervention can prevent serious complications and ensure the airway is cleared effectively․ Proper technique is crucial for safe and successful choking relief․

Head and Spinal Injuries
Head and spinal injuries require immediate, careful handling to prevent further damage․ Immobilization is critical, especially for the neck and spine, to avoid worsening potential harm or paralysis․
Assessing Head Injuries: Symptoms and Care
Assessing head injuries involves checking for symptoms like confusion, dizziness, or loss of consciousness․ Look for visible wounds, swelling, or bleeding․ Important signs include vomiting, blurred vision, or severe headaches․ Immediate care includes immobilizing the head and neck to prevent further damage․ Do not move the injured person unless necessary․ Apply gentle pressure to stop bleeding with a clean cloth; Monitor breathing and consciousness․ Seek professional help immediately if symptoms persist or worsen․ Early intervention is crucial to prevent long-term complications․ Always follow updated 2023 first aid guidelines for accurate assessment and care․
Spinal Injury Management: Do’s and Don’ts
When managing a suspected spinal injury, the priority is to prevent further damage․ Do immobilize the person, keeping their head, neck, and body aligned․ Use a rigid board or sturdy surface for support․ Do not attempt to move the individual unless they are in immediate danger․ Call emergency services promptly․ Avoid removing helmets or gear unless necessary for breathing․ Do not bend or twist the injured area․ Loosen tight clothing around the neck but avoid removing clothing unnecessarily․ Follow 2023 first aid guidelines for proper handling to minimize long-term harm and ensure the best outcomes․

Musculoskeletal Injuries
Musculoskeletal injuries involve damage to muscles, tendons, or bones․ Proper assessment and immediate care are crucial․ Use the RICE method for sprains and strains, while fractures require immobilization․ Always follow 2023 first aid guidelines for effective management and recovery․
Sprains and Strains: RICE Method
The RICE method is a widely recommended approach for managing sprains and strains․ Rest the injured area to prevent further damage․ Apply ice for 15–20 minutes every 1–2 hours to reduce swelling․ Use compression bandages to immobilize and support the injury․ Elevate the affected limb above heart level to minimize swelling․ Early intervention with RICE can significantly improve recovery time․ Monitor for severe pain, numbness, or limited mobility, as these may indicate a more serious injury requiring medical attention․ Always follow 2023 first aid guidelines for proper application of the RICE method․
Fractures: Immobilization and Transport
When dealing with fractures, immobilization is crucial to prevent further injury․ Use splints, rigid materials, or even makeshift supports to keep the affected limb stable․ Avoid moving the injured area unless necessary․ For transport, carefully place the person on a sturdy surface or stretcher, ensuring the fracture remains immobilized․ Do not attempt to straighten or move the limb․ Elevate the injured area if possible to reduce swelling․ Always seek immediate medical attention for proper treatment․ If the fracture is severe or accompanied by deformity, numbness, or inability to move the limb, emergency services should be contacted promptly․
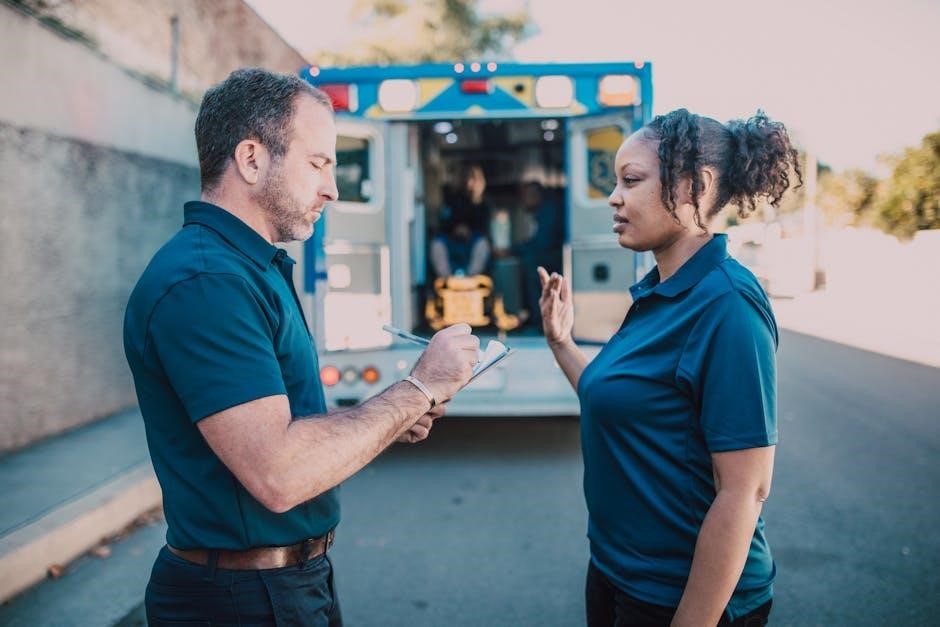

Recovery and Aftercare
Proper recovery involves monitoring for infection, managing pain with OTC medications, and ensuring wounds heal correctly․ Follow medical advice to avoid complications and promote full recovery․
Pain Management: Safe Use of Over-the-Counter Medications
For effective pain management, over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used, but always follow recommended dosages․ Acetaminophen is ideal for mild to moderate pain and fever reduction, while ibuprofen is better for inflammatory pain․ Avoid exceeding the maximum daily dose to prevent liver or stomach damage․ For children, consult a healthcare provider before administering medication․ In cases of chronic pain or prolonged use, seek medical advice․ Never combine medications without professional guidance, and monitor for side effects like stomach upset or drowsiness․ Proper use ensures safety and effectiveness in pain relief during recovery․
Monitoring for Infection: Signs and Prevention
Monitoring for infection is crucial after an injury or illness․ Signs include redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or a foul odor at the site, as well as fever or chills․ To prevent infection, clean wounds with soap and water, apply antiseptic solutions, and cover with sterile dressings․ Change dressings daily or if soiled․ Avoid touching the wound unnecessarily, and ensure hands are clean․ If signs of infection appear, seek medical attention promptly․ Regular monitoring helps identify complications early, ensuring proper treatment and preventing severe outcomes․ Always follow hygiene practices to minimize infection risks and promote healing․
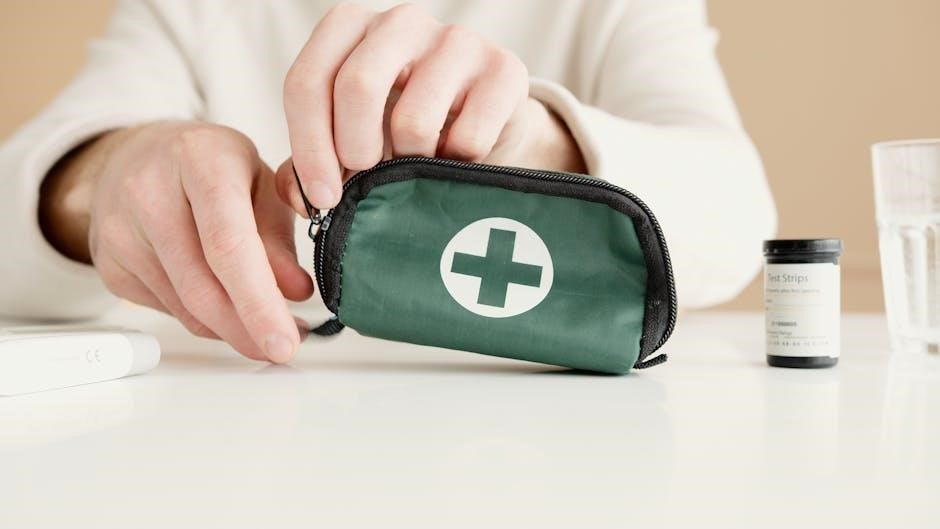

Preventing Accidents and Injuries
Preventing accidents and injuries requires proactive measures like identifying hazards, ensuring proper training, and maintaining safe environments․ Regular safety drills, updated first aid kits, and awareness campaigns are essential․ Encourage a culture of safety, promote preparedness, and address risks before they escalate to ensure well-being and minimize emergencies․ Stay informed about potential dangers and take steps to mitigate them effectively․ Prevention is the first line of defense in safeguarding health and reducing the need for emergency interventions․ Always prioritize caution and planning to create safer spaces for everyone․
Home Safety Tips
Ensuring home safety is crucial for preventing accidents and injuries․ Regularly inspect your living space to identify potential hazards, such as loose wires or slippery floors․ Secure heavy furniture and appliances to prevent tip-overs, and install safety gates at stairs․ Keep emergency exits clear and ensure all family members know the escape routes․ Store chemicals and medications out of reach of children, and label them clearly․ Install smoke detectors and carbon monoxide alarms, and test them monthly․ Maintain a well-stocked first aid kit and post emergency contact numbers prominently․ Educate everyone on proper fire extinguisher use and conduct regular safety drills․
Workplace Safety Measures
Implementing workplace safety measures is essential to prevent accidents and ensure a secure environment․ Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential hazards and develop strategies to mitigate them․ Establish clear safety protocols and provide comprehensive training for all employees․ Ensure emergency exits are unobstructed, and first aid kits are easily accessible․ Promote a culture of safety by encouraging employees to report incidents or near-misses without fear of repercussions․ Use personal protective equipment (PPE) where necessary and maintain proper maintenance of tools and machinery․ Stay updated with occupational safety regulations and adapt policies to comply with the latest standards․ Regular drills can enhance preparedness for emergencies․

Legal Aspects of First Aid
Understand the legal frameworks governing first aid, including Good Samaritan laws and duty of care․ Employers must provide adequate first aid resources, while individuals should know their responsibilities and limitations to avoid liability․ Stay informed about updates to ensure compliance and protect both the provider and recipient in emergency situations․
Good Samaritan Laws
Good Samaritan laws protect individuals who provide first aid in emergencies from legal liability․ These laws vary by jurisdiction but generally shield bystanders acting in good faith․ They aim to encourage assistance without fear of legal consequences․
Typically, protections apply when aid is given voluntarily, without recklessness or gross negligence․ These laws promote community support and timely intervention, ensuring helpers are not deterred by legal concerns․ Understanding these protections is crucial for first aid providers․ Stay informed about local regulations to act confidently in emergencies․ These laws foster a culture of safety and mutual aid․
Liability and Duty of Care
Liability and duty of care in first aid refer to the legal responsibility to provide reasonable assistance in emergencies․ While Good Samaritan laws protect well-intentioned actions, providers must act within their training and avoid gross negligence․ A duty of care exists when a person assumes responsibility for another’s well-being, such as administering first aid․ Failure to meet this duty can result in legal consequences․ Proper training and adherence to guidelines help minimize liability risks․ Understanding these principles is essential for first aid providers to balance compassion with legal and ethical obligations, ensuring they act responsibly while helping others in need․ Proper protocols reduce risks․

Mental Health First Aid
Mental Health First Aid focuses on recognizing signs of distress, providing emotional support, and connecting individuals to professional help․ Training enhances skills to address crises effectively․
Recognizing Signs of Distress
Recognizing signs of distress is crucial in mental health first aid․ Emotional changes, such as withdrawal or mood swings, and behavioral changes, like altered eating or sleeping patterns, may indicate distress․ Physical signs, including rapid breathing or trembling, can also signal emotional turmoil․ It’s important to approach the individual with empathy, listen actively, and avoid judgment․ Encouraging open conversation helps identify underlying issues․ Assessing the severity of the situation determines if professional intervention is needed․ Early recognition and supportive responses can significantly impact recovery and well-being, making mental health first aid an essential skill for everyone․
Supporting Someone in Crisis
Supporting someone in crisis requires a calm and empathetic approach․ Ensure their safety and create a comfortable environment․ Listen actively without judgment, validating their feelings to build trust․ Avoid minimizing their concerns or offering unsolicited advice․ Encourage them to express emotions openly and provide reassurance․ Maintain a non-threatening posture and tone of voice․ If necessary, guide them to professional help, respecting their autonomy․ Stay patient and supportive, understanding that recovery is a process․ Remember, your role is to provide emotional support, not to solve the crisis alone․ Knowing when to seek additional resources is key to effective mental health first aid;
Specialized First Aid Scenarios
Specialized first aid scenarios require tailored approaches for unique situations, such as paediatric or geriatric care, ensuring age-specific techniques and addressing diverse needs effectively in emergencies․
Paediatric First Aid
Paediatric first aid focuses on providing immediate care to infants and children during medical emergencies․ It involves techniques tailored to their smaller body size and developmental stage․ Common scenarios include burns, falls, and choking․ Proper airway management and CPR methods differ from adult care․ Training emphasizes assessing the child’s condition, maintaining calm, and using appropriate equipment․ Understanding child-specific symptoms, such as respiratory distress or altered consciousness, is crucial․ Immediate action can prevent long-term harm, making paediatric first aid a vital skill for caregivers and professionals․ Regular updates ensure adherence to the latest guidelines, enhancing outcomes for young patients in critical situations․
Geriatric First Aid
Geriatric first aid addresses the unique needs of elderly individuals, focusing on common injuries like fractures, burns, and sprains․ It emphasizes gentle handling to avoid further harm․ Key considerations include managing chronic conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, and being aware of medication interactions․ Techniques include proper lifting to prevent spinal strain and using supportive devices․ Creating a safe environment to prevent falls is crucial․ First responders should monitor for signs of shock or confusion and provide reassurance․ Regular updates in geriatric care ensure tailored approaches, improving outcomes for older adults in emergency situations while respecting their dignity and specific health needs․
First aid training is crucial for saving lives and reducing injury severity․ Regular updates ensure effectiveness, fostering a safer, more prepared community․ Stay informed, act confidently, and prioritize care․
Importance of Regular Training and Updates
Regular first aid training ensures individuals stay updated on the latest techniques and protocols, enhancing their ability to respond effectively in emergencies․ Updates in 2023 guidelines reflect advancements in medical care, addressing new challenges and improving outcomes․ Continuous education helps retain knowledge and builds confidence, enabling prompt and appropriate actions․ Staying informed about changes in first aid practices is vital for adapting to evolving scenarios and equipment․ By prioritizing training, communities can foster a culture of preparedness, reducing risks and saving lives․ Regular updates also address common mistakes and refine best practices, ensuring care is both safe and effective in real-world applications․
Encouraging Community Participation in First Aid
Active community involvement in first aid is crucial for building a resilient society․ By organizing workshops, demonstrations, and awareness campaigns, individuals can learn lifesaving skills․ Schools, workplaces, and public spaces should integrate first aid training into their programs․ Encouraging participation fosters a culture of readiness and empathy․ Recognition of volunteer first responders and community champions can inspire others to get involved․ Collaboration with local organizations and healthcare providers further strengthens these efforts․ Regular events and accessible resources, such as free training sessions, ensure widespread engagement․ Together, communities can create a network of trained individuals prepared to act in emergencies․

